Experimental Nuclear and Subnuclear Physics: PANDA
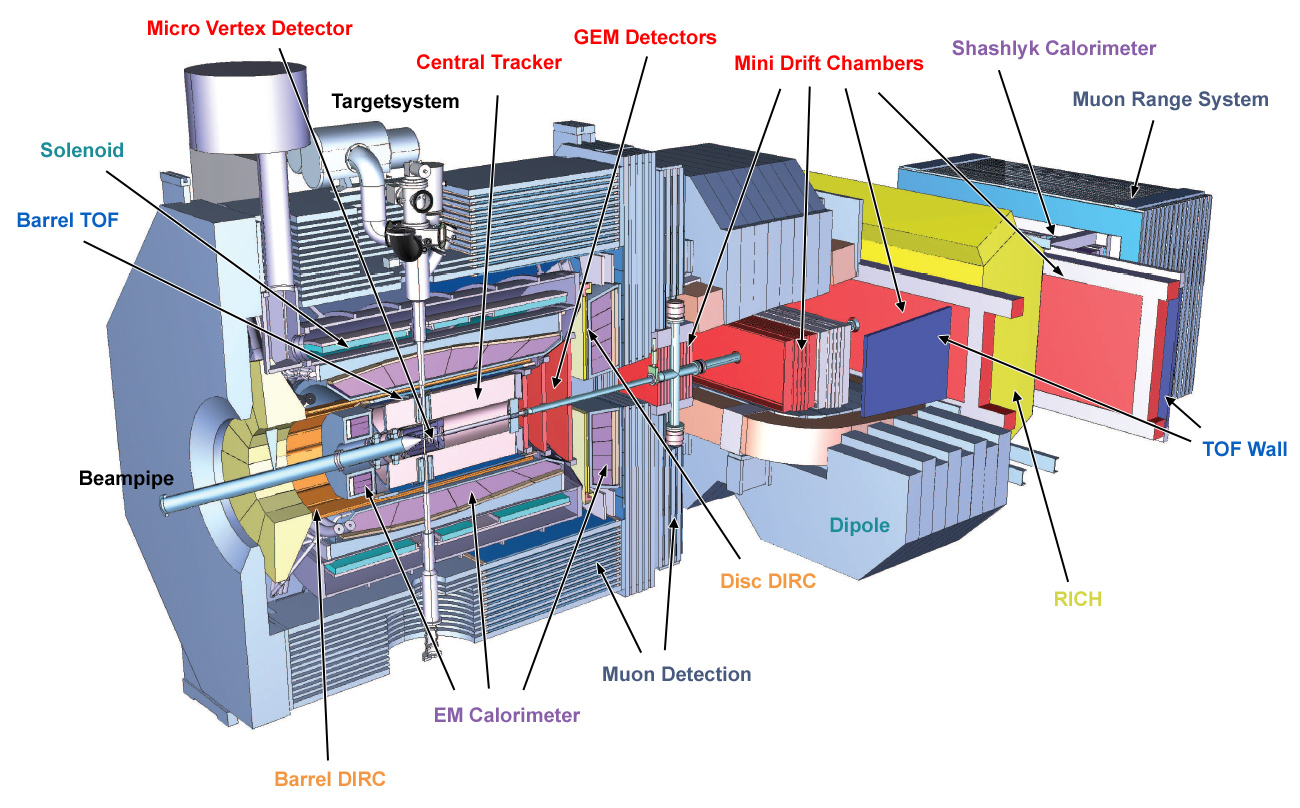
PANDA is a fixed target experiment that uses an antiproton beam impinging on a proton target with cms energies ranging from 2.25 to 5.47 GeV. It will run in 2018 in a new accellerator facility (FAIR) that is being build at the GSI laboratory, in Darmstadt, Germany. The antiproton beam will be produced at high intensity (maximum luminosity in PANDA apparatus is 2x10**32 cm-2sec-1) or with high resolution (percentage resolution on beam momentum = 3x10**(-5) ). Besides the proton fixed target (frozen hydrogen) nuclear targets are forseen (for instance frozen deuterium and neon). PANDA can study a wide range of physics topics, like for instance :
- study of production and decay of exotic bound states (non qqbar mesons) containing charm (like the Z_c(3900) recently discovered at BES) or without charm content (glueballs, oddbals, hybrids, molecules);
- studies of non-perturbative QCD (p_bar p cross section; strange baryon production and their sopin correlations);
- study of the influence of the nuclear potential on the masses of mesons produced in nuclear targets;
- detection of the double strange hypernuclei;
- form factors (Drell-Yan) and electromagnetic processes;
- study of CP-violation in charm mesons; production of charm baryons; charm rare and forbidden decays.
The Pavia group is involved mainly in the software development in two areas of interest. The first is the implementation of the algorithms for the track reconstruction (pattern recognition, track fitting, Kalman filter) in the central detector. The Pavia group is also responsible of the coordination of the pattern recognition of the entire detector. The second is the resposability of the maintenance of the track following package (GEANE), used in the Kalman filter procedure. That implies the interaction also with the CERN software group; in factthe official GEANT - GEANE repository resides at CERN.
Staff: Gianluigi Boca, Alberto Rotondi